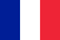
Foot fungus is a common name for several types of dermatomycosis, which differ in the location and type of fungus. There are four main groups of foot mycosis:
- skin of interdigital spaces;
- toes;
- toenails (onychomycosis);
- skin of the lower limbs.
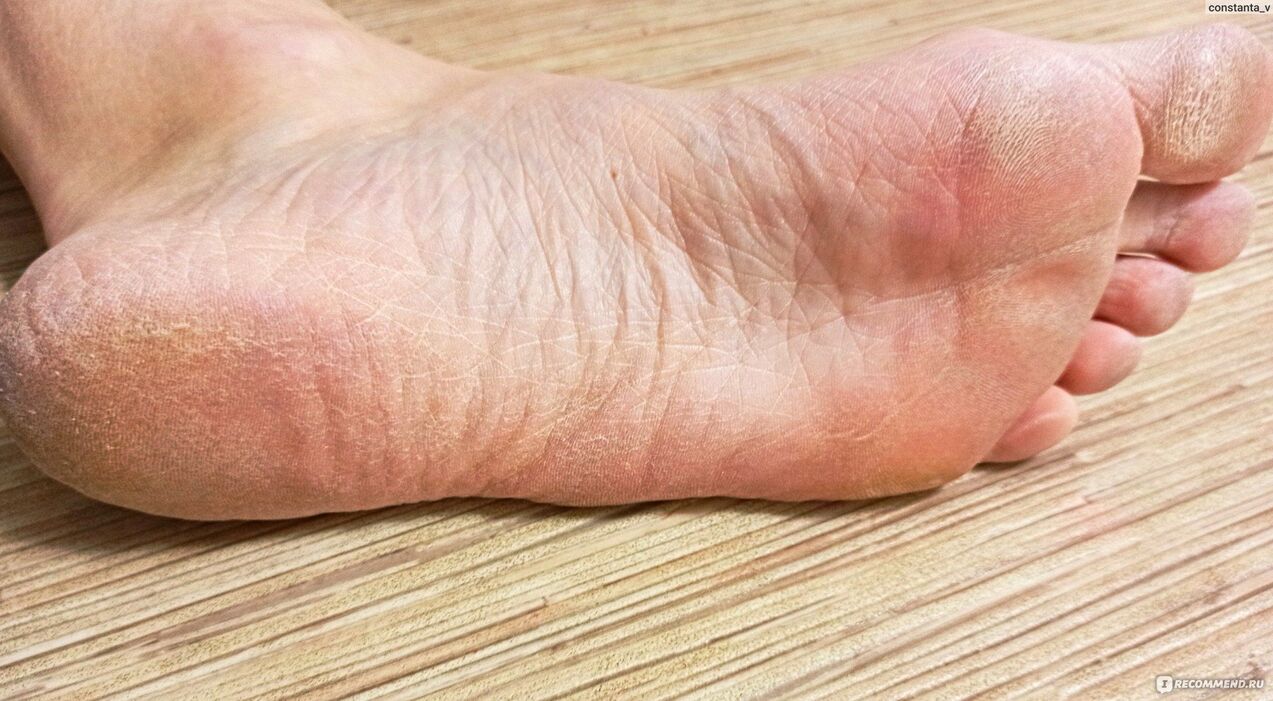
What is foot mycosis?
If you believe the statistics, in our country foot fungus is diagnosed in almost twenty percent of the population. Fungal infections live freely in the environment and sometimes we don't even realize that we may be carriers of the disease.
Under certain favorable conditions, some of the almost five hundred species of fungi existing in nature experience a "moment of rebirth". They multiply rapidly, forming numerous colonies and spreading the spores to new areas of the skin.
Fungal waste products are toxic. Due to intoxication, the entire body as a whole can suffer.
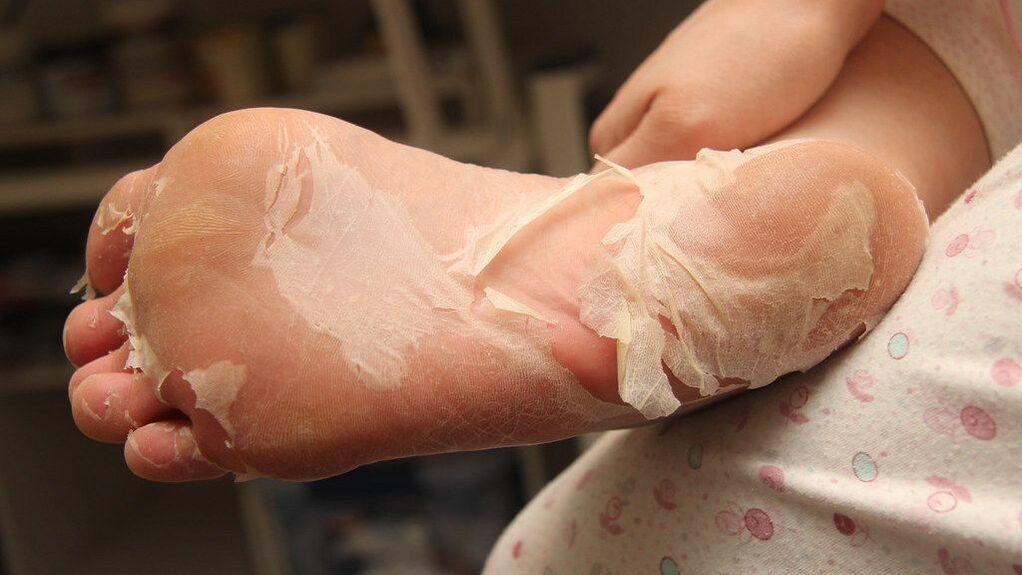
Mycosis of the feet is caused by microscopic fungi:
- dermatophytes;
- yeast;
- moldy;
- candida.
Prerequisites for the appearance of foot fungus:
- visit a swimming pool, sauna, bathhouse, gym, wherever it is necessary to move barefoot and there is also a risk of illness while working;
- use someone else's shoes;
- dermatological diseases (neurodermatitis, psoriasis, eczema);
- chronic organic diseases;
- diabetes mellitus (diabetic foot) and other endocrine disorders;
- flat feet with big toe deformity;
- increased sweating of the skin of the feet (hyperhidrosis);
- decrease in the body's defenses, especially in people with nail fungus (onychomycosis);
- uncontrolled use of antibiotics, hormones and anti-allergic drugs;
- lesions to the skin of the feet in the form of cracks, corns and calluses.
What does foot fungus look like?
The disease manifests itself depending on the type of fungus that has "infected" the skin of the feet and the exact location in which it is found.
Very often the symptoms of the disease (desquamation, layering of scales, severe itching) manifest themselves with the addition of an inflammatory process due to scratching.
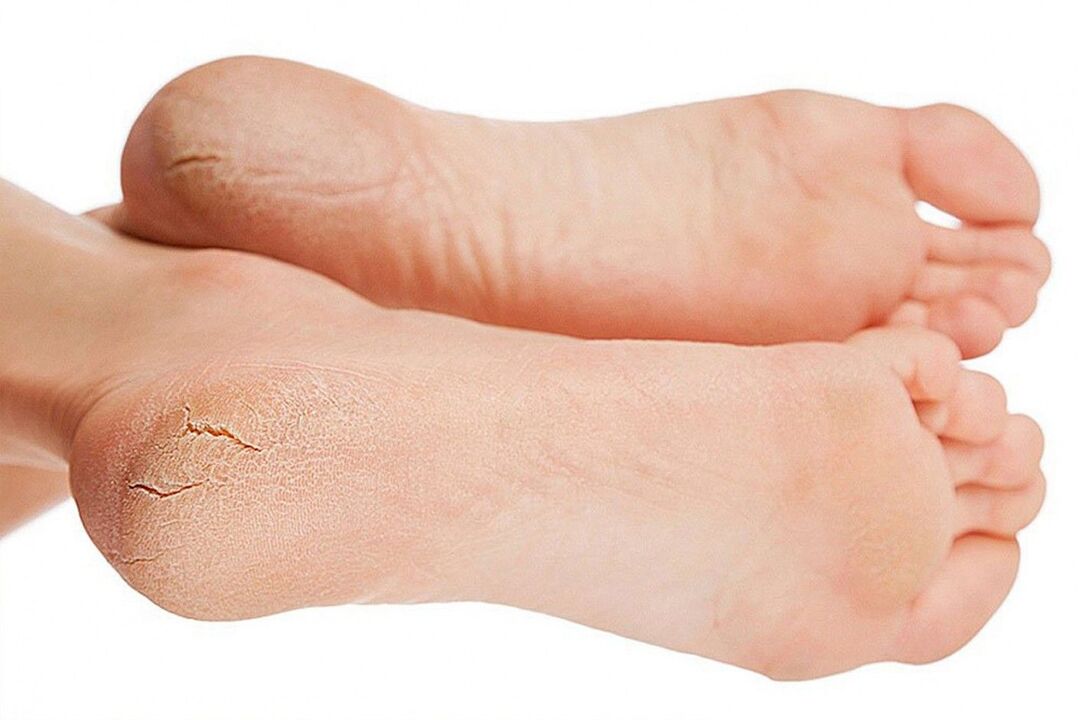
Fungal infection of the skin and toenails has two forms: acute and chronic. In the acute form, recovery usually occurs within a few days (taking into account the adequacy of the prescribed drugs). The chronic form is not completely cured; alternates relapses and remissions. Its treatment is aimed at alleviating the symptoms of the disease.
Important! As soon as you suspect the first signs of foot fungus, rush to the doctor! Do not self-medicate, delaying the spread of the infection. The longer the visit to a specialist is delayed, the longer the treatment will take.
Foot fungus between toes
The infection, as a rule, first affects the interdigital folds (especially the narrowest ones between the third and fourth toes).
Signs of interdigital foot fungus:
- thickened skin is dry;
- furrows and even calluses form;
- the skin on the feet cracks and peels;
- pain and debilitating itching appear.
It happens that the fungus is hidden and manifests itself only with the formation of small cracks between the fingers, slight peeling and mild itching. The patient does not seek help from doctors for a long time and only when he starts crying does he start to worry.
The exudative (wetting) form of foot fungus is:
- intertriginous, which presents as diaper rash;
- dyshidrotic - with the appearance of blisters;
- mixed - interginous-dyshidrotic.
The most dangerous form of fungal infection is considered to be vesicular foot fungus or dyshidrotic mycosis.
It is characterized by the formation of painful blisters (large blisters) that fuse together and form large erosive areas without skin lining. As it develops, the erosion steadily increases in volume. The fluid inside the blisters is highly contagious. You can infect all family members at once.
The foot, being practically devoid of skin, also runs the risk of "catching" a serious purulent infection. Recovery is delayed by at least three to four months. The site of localization is usually the skin of the instep, somewhat less often the skin between the toes and even less often the skin on the surface of the heel.
Fungus on toes
An untreated fungus "crawls" from the interdigital space to the nearest fingers. In principle, all the characteristic symptoms of fungal infection of the interdigital folds are also inherent in the skin of the toes: severe itching, etc. They cause a lot of inconvenience.
As a result of endless scratching, the skin on the fingers thickens, becomes inflamed and acquires a bright red color. Persistent swelling, pustules and blisters appear. A pustular rash usually forms due to a bacterial infection.
Almost always, the process that occurs on or between the skin of the fingers extends to the nails.
Onychomycosis or nail fungus
The main causative agent of the disease is dermatophytes and at least fungi of the genus Candida. The appearance of the nail and sensations with onychomycosis are not the most pleasant.
Signs of the disease:
- deformation and separation of the nail;
- pain when walking;
- the appearance of cloudiness and a yellowish tint on the nail;
- significant thickening of the nail plate;
- destruction of nails.
Important! Onychomycosis contributes to the transition of any fungal disease into a chronic form. Do not delay the visit to the doctor, because fungal spores can spread further to the extremities: legs, thighs and even buttocks, abdomen and chest.
Foot fungus: causes and symptoms of the disease in a child
Fungi occur on children's feet for several reasons:
- endocrine disorders;
- uncomfortable shoes, made of imitation leather, that don't fit well;
- improper functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- dirty, uncut toenails;
- negligence of personal hygiene rules when visiting bathhouses and gyms;
- flat feet.

Most often, the fungus affects the skin of children in the spaces between the fingers. Symptoms: scaling, thickening of the nail plate tissue, severe itching. Small erosions and ulcers appear, inflammation of the skin of the foot.
Diagnosis foot mycosis
Correct treatment of mycosis of the feet and its diagnosis can only be carried out by a dermatologist.
What a doctor should do when diagnosing foot fungus:
- detailed examination of the patient's foot;
- anamnesis collection (a survey is conducted on the symptoms of the disease, as well as the presence or absence of chronic diseases, heredity);
- scraping the affected skin or cutting off a piece of deformed nail;
- a special test to confirm the presence of a fungal infection in the body as a whole;
- sow the material on a nutrient medium (if necessary);
- skin biopsy (a small piece of affected skin is cut) for examination under a microscope (carried out in exceptional cases);
- General and biochemical blood test.
To perform the test correctly you need:
- do not use antifungal agents without a doctor's prescription;
- do not treat the affected skin with anything at least three days before the test;
- It is recommended to use only baby soap without additives;
- do not carry out nail removal manipulations for a week;
- do not take medications;
- if possible, do not smoke;
- Before taking a blood test, do not drink coffee, lemonade, or alcohol.
How and with what to treat foot mycosis
The treatment prescribed by the doctor is usually complex, consisting of tablets and local products (creams, ointments, sprays). Treatment of foot fungus with folk remedies should not be ignored. They will be able to speed up the healing process of injuries. It is impossible to name an effective remedy that can be used against foot fungus, because during treatment it is important to achieve an antifungal effect, eliminate concomitant pathologies and improve blood supply to the feet.
They have an excellent therapeutic effect:
- A broad-spectrum antifungal is a great remedy for foot fungus. It is the basis for many antifungal drugs. For local use only. Effective as an ointment, cream, lotion, aerosol. The ointment should be applied in a thin layer to the clean, dry soles of the feet three times a day. It is best to use a month or two after treatment.
- A product (lotion) to restore and protect the nail plate in case of fungal infection. This spray has been proven effective against foot fungus. It mainly serves to prevent fungal diseases. Contains undecylenic acid, which forms immunity against fungal nail diseases. The spray is very easy to apply. It is used on the inside surface of shoes to disinfect them. But a patient with onychomycosis still needs to be treated using not only this, but also other antifungal drugs.
- Antifungal drug for systemic use.""On the ground" kills mushrooms of all types. It is used in the form of tablets, cream, spray and solution for oral administration. For adults, the tablets are prescribed for two weeks, to be taken twice a day. Cream against fungus on the skin of the foot is rubbed into the damaged areas twice a day. The duration of treatment can vary from a week to a month and a half.
- Antifungal antibiotic. The drug inhibits the proliferation of fungi. Available in the form of tablets, oral suspension and ointment. The ointment is indicated for use only in cases where the nail is not affected by fungi of the genus Candida.The tablets are taken for three months. The first month - once a day, the second and third - every other day. The dosage is prescribed by the doctor. The drug ends when healthy nails grow back.
- Antifungal drug. It has a high degree of activity against all groups of fungal organisms that can cause foot fungus. It is available in suppositories and tablets, but is used to treat fungal infections of the intestines and female genital organs. It is recommended to apply the ointment once or twice a day for up to a month.
How to treat foot fungus at home
It is possible and necessary to cure a fungal "infection" at home, but only after consulting a doctor and having with you the test results and a set of individually selected special drugs. Traditional medicine also treats foot fungus, but is usually used only as an additional treatment:
Baking soda is used against foot fungus as a softener (for a sore toenail). Place your feet in a soda solution (prepared at the rate of one teaspoon per liter of warm water) for 7-9 minutes. From a cotton pad we form a plate corresponding to the size of the nail. Dip a cotton pad in a 3% hydrogen peroxide solution and place it on a soft nail. Wrap the compress in cling film or place it on your fingertip. Keep the cotton ball on the nail for 45-60 minutes. We repeat the manipulation twice a day. If you experience a burning sensation, rinse your finger with water. You will see the effectiveness of the procedure within four days.

Treating foot fungus with wine vinegar is a simple and economical remedy. At night, wash your feet with warm water without soap and place them in a basin with a strong solution of wine vinegar. After five minutes, dry your feet and put on socks previously soaked in this solution. The procedure has a disinfectant effect. A simple recipe for treatment at home is a bath with soluble coffee. Prepare strong coffee in the required amount of water. The drink is allowed to cool slightly and the feet are steamed. Regularly - twice a day - the unpleasant odor of the feet is eliminated and the mycosis is "expelled".
Rules for caring for personal belongings during illness:
- slippers must have closed toes and heels;
- you cannot walk barefoot;
- shoes should be treated with antifungal agents twice a day, for example: a 40% solution of acetic acid;
- wash personal items separately from others;
- Wash bathtubs, sinks, shower cabins with disinfectant solutions after use;
- Daily water cleaning of the apartment and ventilation of the room is required;
- daily change of socks;
- After recovery, get rid of old underwear, shoes and medications.
Prevention of foot and nail fungus
To the question "How not to get sick? " the answers are simple:
- maintain personal hygiene;
- stick to a dairy- and vegetable-based diet, eat more fruits and vegetables;
- abandon bad habits;
- control your emotional state, pay attention to stress;
- engage in physical education and outdoor sports.